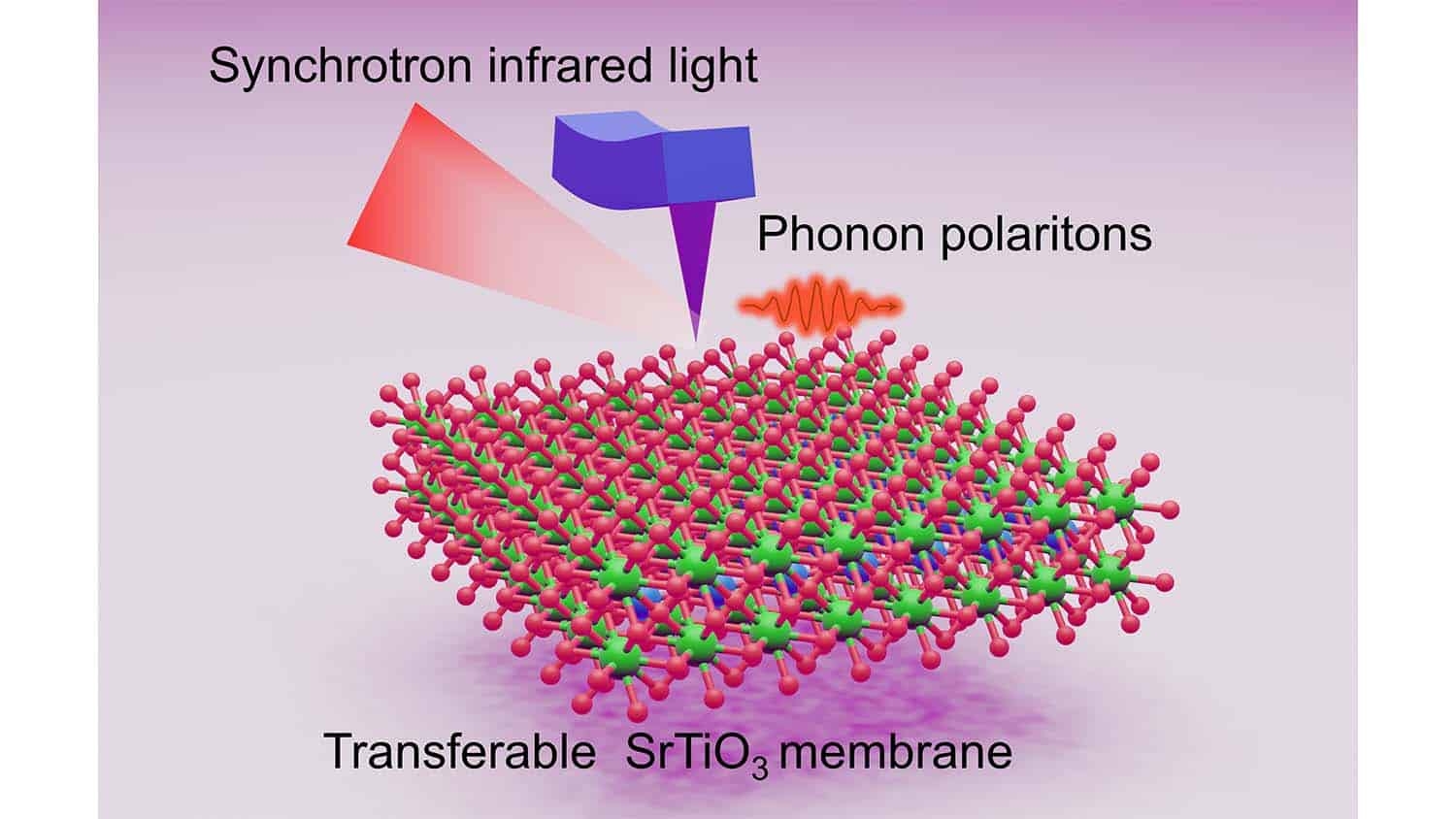
Researchers have for the first time demonstrated that a specific class of oxide membranes can confine, or “squeeze,” infrared light – a finding that holds promise for next generation infrared imaging technologies. The thin-film membranes confine infrared light far better than bulk crystals, which are the established technology for infrared light confinement.
“The thin-film membranes maintain the desired infrared frequency, but compress the wavelengths, allowing imaging devices to capture images with greater resolution,” says Yin Liu, co-corresponding author of a paper on the work and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at North Carolina State University.
“We’ve demonstrated that we can confine infrared light to 10% of its wavelength while maintaining its frequency – meaning that the amount of time that it takes for a wavelength to cycle is the same, but the distance between the peaks of the wave is much closer together. Bulk crystal techniques confine infrared light to around 97% of its wavelength.”
“This behavior was previously only theorized, but we were able to demonstrate it experimentally for the first time through both the way we prepared the thin-film membranes and our novel use of synchrotron near-field spectroscopy,” says Ruijuan Xu, co-lead author of the paper and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at NC State.
For this work, the researchers worked with transition metal perovskite materials. Specifically, the researchers used pulsed laser deposition to grow a 100-nanometer thick crystalline membrane of strontium titanate (SrTiO3) in a vacuum chamber. The crystalline structure of this thin film is high quality, meaning that it has very few defects. These thin films were then removed from the substrate they were grown on and placed on the silicon oxide surface of a silicon substrate.
The researchers then made use of the technology at the Advanced Light Source of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory to perform synchrotron near-field spectroscopy on the strontium titanate thin film as it was exposed to infrared light. This enabled the researchers to capture the interaction of the material with infrared light at the nanoscale.
To understand what the researchers learned, we need to talk about phonons, photons and polaritons. Phonons and photons are both ways that energy travels through and between materials. Phonons are essentially the waves of energy caused by how atoms vibrate. Photons are essentially the waves of electromagnetic energy. You can think of phonons as units of sound energy, whereas photons are units of light energy. Phonon polaritons are quasi particles that occur when an infrared photon is coupled with an “optical” phonon – meaning a phonon that can emit or absorb light.
“Theoretical papers proposed the idea that transition metal perovskite oxide membranes would allow phonon polaritons to confine infrared light,” Liu says. “And our work now demonstrates that the phonon polaritons do confine the photons, and also keep the photons from extending beyond the surface of the material.
“This work establishes a new class of optical materials for controlling light in infrared wavelengths, which has potential applications in photonics, sensors and thermal management,” Liu says. “Imagine being able to design computer chips that could use these materials to shed heat by converting it into infrared light.”
“The work is also exciting because the technique we’ve demonstrated for creating these materials means that the thin films can be easily integrated with a wide variety of substrates,” Xu says. “That should make it easy to incorporate the materials into many different types of devices.”
The paper, “Highly Confined Epsilon-Near-Zero- and Surface-Phonon Polaritons in SrTiO3 Membranes,” is published in the open access journal Nature Communications. Co-lead author of the paper is Iris Crassee of the University of Geneva. Co-corresponding author of the paper is Alexey Kuzmenko of the University of Geneva. The paper was co-authored by Yixi Zhou, Adrien Bercher, Lukas Korosec, Carl Willem Rischau and Jérémie Teyssier of the University of Geneva; Hans Bechtel and Stephanie Gilbert Corder of the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Kevin Crust, Yonghun Lee, Jiarui Li and Harold Hwang of Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory; and Jennifer Dionne of Stanford University
The research was done with support from the U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Sciences, Division of Materials Sciences and Engineering, under contract no. DE-AC02-76SF00515; and by the National Science Foundation under grant number 2340751.
-shipman-
Note to Editors: The study abstract follows.
“Highly Confined Epsilon-Near-Zero- and Surface-Phonon Polaritons in SrTiO3 Membranes”
Authors: Ruijuan Xu and Yin Liu, North Carolina State University; Iris Crassee, Yixi Zhou, Adrien Bercher, Lukas Korosec, Carl Willem Rischau, Jérémie Teyssier and Alexey B. Kuzmenko, University of Geneva; Hans A. Bechtel and Stephanie N. Gilbert Corder, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory; Kevin J. Crust, Yonghun Lee, Jiarui Li and Harold Y. Hwang, Stanford University and the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory; and Jennifer A. Dionne, Stanford University
Published: June 4, Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-47917-x
Abstract: Recent theoretical studies have suggested that transition metal perovskite oxide membranes can enable surface phonon polaritons in the infrared range with low loss and much stronger subwavelength confinement than bulk crystals. Such modes, however, have not been experimentally observed so far. Here, using a combination of far-field Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy and near-field synchrotron infrared nanospectroscopy (SINS) imaging, we study the phonon-polaritons in a 100 nm thick freestanding crystalline membrane of SrTiO3 transferred on metallic and dielectric substrates. We observe a symmetric-antisymmetric mode splitting giving rise to epsilon-near-zero and Berreman modes as well as highly confined (by a factor of 10) propagating phonon polaritons, both of which result from the deep-subwavelength thickness of the membranes. Theoretical modeling based on the analytical finite-dipole model and numerical finite-difference methods fully corroborate the experimental results. Our work reveals the potential of oxide membranes as a promising platform for infrared photonics and polaritonics.
This post was originally published in NC State News.
- Categories: